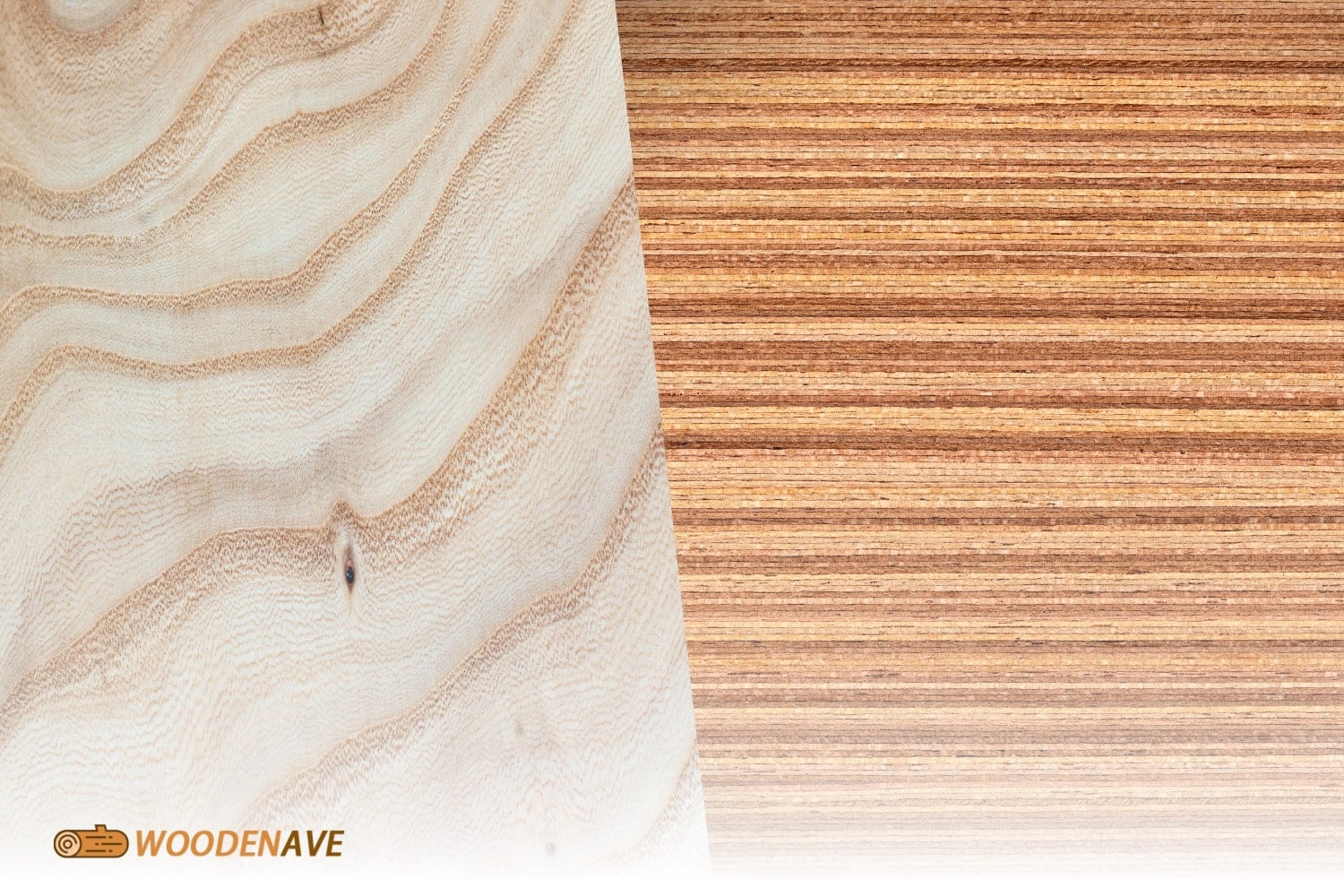

Natural wood veneer is sliced directly from logs, showing off the natural beauty of real wood, whereas engineered wood veneer is produced through a more complicated process that reconstitutes wood fibers to create a uniform appearance. So, the primary difference between natural and engineered wood veneer lies in their origin and manufacturing processes.
This article will dive into the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of both types of veneer, to help you make an informed decision for your projects. WoodenAve offers a variety of options in both categories, catering to diverse aesthetic and functional needs.
Key Takeaways
- Natural wood veneer is sourced from real logs, offering distinct grain patterns.
- Engineered wood veneer is made from reconstituted wood fibers, providing consistency in appearance.
- The manufacturing process for natural veneer involves slicing logs, while engineered veneer uses fast-growing trees.
- Cost tends to be lower for engineered veneers due to efficient production.
- Sustainability practices differ between the two types, with engineered options often being more eco-friendly.
What is Natural Wood Veneer?
Natural wood veneer is a thin layer of real wood that has been sliced or peeled from logs. Each sheet has the unique characteristics of the tree species from which it originates. The manufacturing process retains the natural beauty and imperfections of the wood, such as knots and grain variations. This authenticity makes natural veneer popular for high-end furniture and architectural applications.
Natural wood veneers are usually produced from precious wood species like cherry, walnut, or oak. The aesthetic appeal of natural veneers lies in their ability to bring warmth and character to any space. The texture and color of each veneer sheet can vary based on factors such as geographic location and environmental conditions, resulting in a solid wood grain product that is truly one of a kind.
What is Engineered Wood Veneer?
Engineered wood veneer, also known as reconstituted veneer or recomposed veneer, is manufactured by processing thin sheets of fast-growing tree species. This type of reconstituted wood veneer involves cutting and dyeing wood fibers before gluing them together to form blocks.
These thick veneer engineered hardwood flooring blocks are then sliced into sheets that can mimic the appearance of various natural types of wood. The engineered veneer manufacturing process allows for greater consistency in color and grain patterns compared to natural veneers.
This uniformity makes engineered veneers a great choice for large-scale projects where matching aesthetics across multiple surfaces is important. Also, engineered wood flooring veneers can be designed to look like rare or precious wood species without the associated cost or environmental impact.
Natural Veneer vs. Engineered Wood Veneer
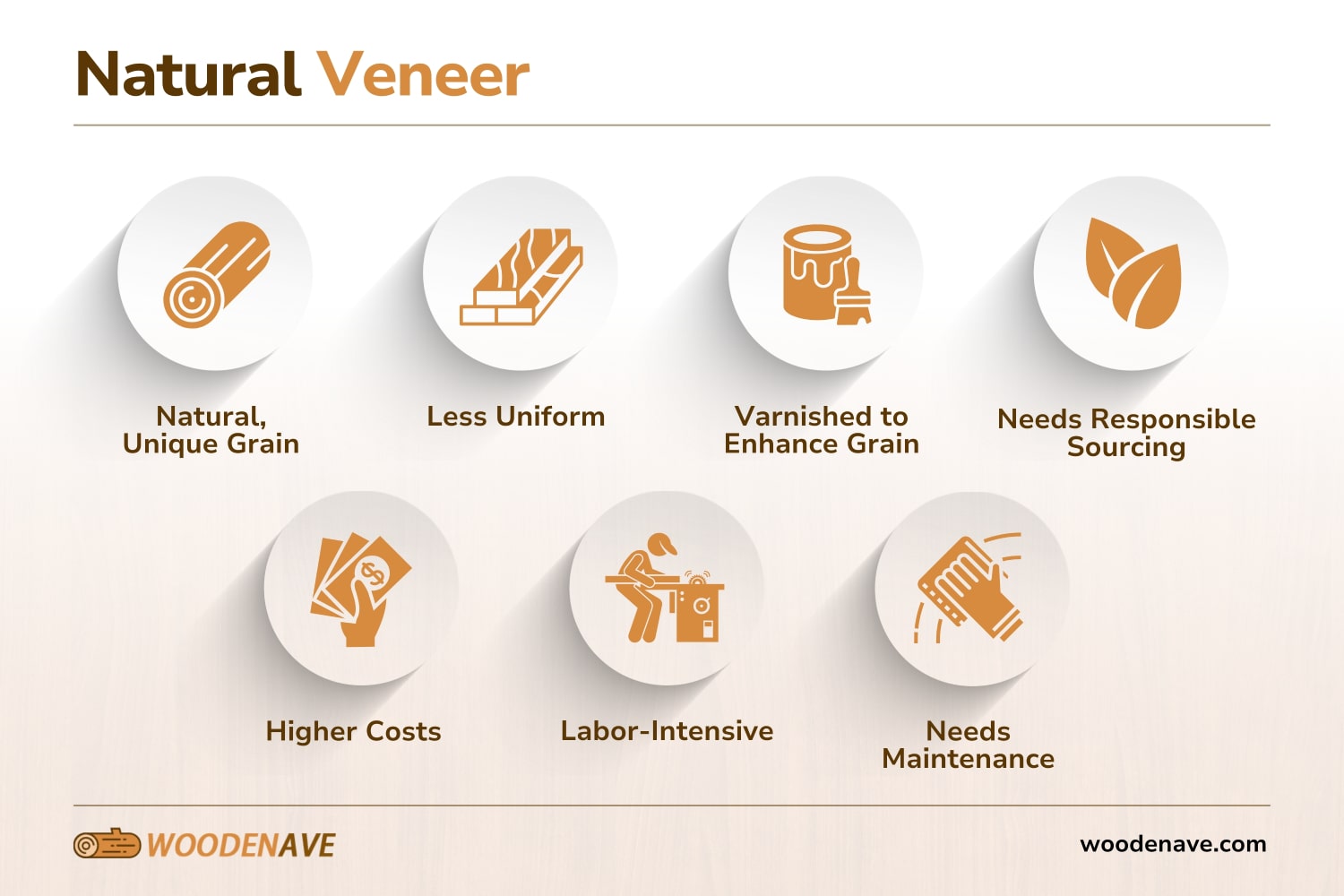
Natural veneer has a much more authentic look, while engineered wood gives you a uniform appearance. Now, it’s time for us to compare solid hardwood vs. engineered hardwood! Below are the main differences between these two in terms of manufacturing process, look and feel, consistency, quality, finish, sustainability, cost, maintenance, and longevity.
| Factor | Natural Veneer | Engineered Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Natural grain; sliced from quality logs | Dyed, glued, and re-sliced for uniformity |
| Look and Feel | Unique grain; authentic imperfections | Uniform; imitates wood styles |
| Consistency | Less uniform; adds character | Consistent color; ideal for large jobs |
| Finish | Varnished to enhance grain | Varnished; added synthetic durability |
| Sustainability | Needs responsible sourcing | Uses fast-growing trees |
| Cost | Higher cost due to rarity; labor-intensive | Lower cost due to efficient production |
| Maintenance | Needs upkeep; can be refinished | Low upkeep; limited refinishing |
Manufacturing Process
Natural veneer is produced by selecting high-quality logs from various tree species. These logs are then sliced into thin natural veneer sheets using specialized equipment that maintains the integrity of the natural wood grain from the core species used. This process preserves the unique characteristics inherent in each log, resulting in sheets that display natural defects — such as knots and mineral streaks — adding to their authenticity and charm.
On the other hand, when looking at engineered hardwood vs. natural, engineered veneer goes through a more complicated manufacturing process designed for efficiency and consistency. This means that your veneer may be produced faster. Fast-growing tree species are harvested and sliced into thin sheets before being dyed in vats to get the desired colors.
These dyed sheets are glued together into blocks that can be shaped according to design specifications. Once these blocks are formed, they are re-sliced into engineered veneer sheets. This renewable engineered veneer imitates various natural wood patterns while minimizing waste during production.
Look and Feel
Natural wood veneer offers an unmatched look and feel due to its authentic characteristics. Each sheet has distinct grain patterns and colors that are the same as the tree species it comes from. The texture often includes natural blemishes like knots, pitch pockets, or mineral deposits that add depth and interest.
This authenticity appeals to those who appreciate the beauty of real wood in their interiors. If this look is important to you when considering engineered veneer and natural veneer types of wood, then natural is the way to go!
Engineered sheets of wood provide a different aesthetic experience, characterized by their uniformity and smoothness. While this veneer can effectively imitate different types of natural wood grains, it doesn’t have all of the unique textures found in genuine wooden surfaces. Engineered slices of veneers usually have fewer surface defects than their natural counterparts, resulting in a cleaner look that suits modern designs focused on minimalism.
Consistency and Quality
The quality of natural veneer can vary based on the log’s origin and how it was processed. Each sheet reflects the qualities of its source tree, which means variations in color, grain pattern, and texture are common. While these differences between the thin veneers add character, they might pose challenges for large-scale projects requiring uniformity across multiple pieces. This is especially true when there are surface knots and other natural dents.
Engineered veneers win in consistency due to their controlled manufacturing processes. Each engineered veneer sheet is designed to have a uniform appearance regarding color and texture, making them great for projects where matching aesthetics across surfaces is crucial. Moreover, the quality control measures applied during production ensure that engineered veneers meet specific standards consistently.
Veneer Finish
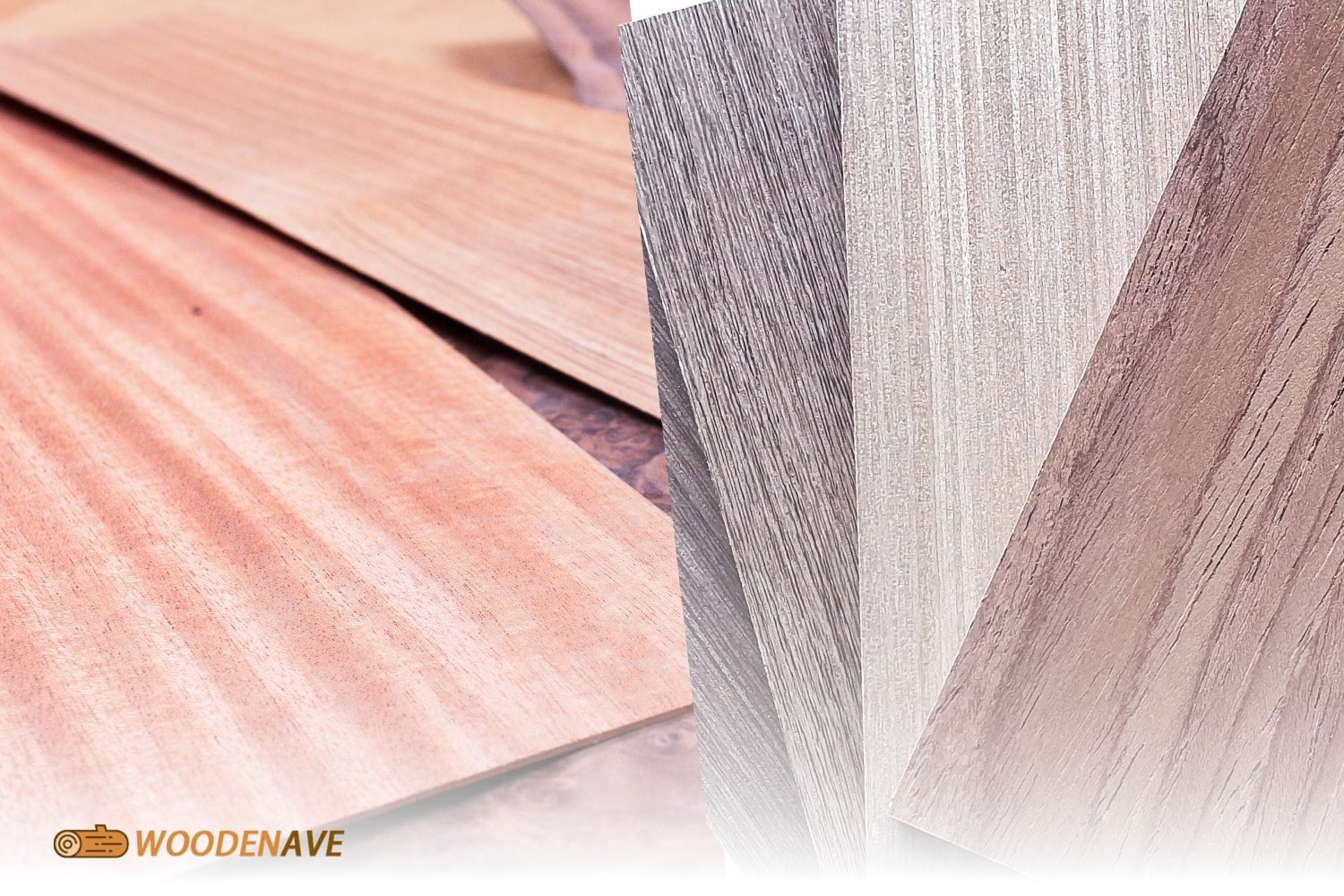

Natural veneers usually benefit from finishing techniques that improve their beauty while protecting them from wear and tear. Common finishes include oil-based varnishes or water-based lacquers that allow the natural characteristics, grain pattern, and features of the wood to shine through while providing durability against scratches or moisture damage.
Natural veneer and engineered veneer go through similar finishing processes. However, engineered wood types frequently use extra treatments designed specifically for synthetic materials. These finishes often improve the durability of the veneer while maintaining a consistent appearance across all surfaces.
Sustainability
Sustainability concerns should play a significant role in your choice between natural and engineered veneers. For natural veneers, there is an issue regarding logging practices required to obtain high-quality timber from mature trees. Responsible sourcing practices — such as those certified by organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) — are essential for ensuring environmental impacts are minimized during harvesting operations.
Man-made veneers are an eco-friendly alternative due to their use of fast-growing tree species that require less time to mature compared with traditional natural wood veneer sheets used for solid lumber products. This approach reduces pressure on old-growth forests and promotes sustainable forestry practices focused on renewable resources for engineered sheets of veneer.
Cost Comparison
Natural veneer generally costs a lot more than other kinds of veneer, whereas engineered veneer is affordable. This is because of factors such as the rarity associated with certain tree species used during production processes, along with labor-intensive techniques required during crafting stages involved in creating these unique thin slices of veneer with natural defects.
On average, engineered wood veneer is one of the cheapest options out there, because of the efficient manufacturing processes used throughout production stages. Also, the reliance upon faster-maturing tree varieties instead of traditional hardwoods requiring longer growth periods before harvest occurs brings the price down.
Maintenance and Longevity
Natural thin sheets of wood veneer usually require regular maintenance — such as cleaning with appropriate products — to look after their integrity over time and maintain their visual appeal for years to come! You can also refinish the beauty of the wood if wear occurs later down the line, meaning you can retain the natural wood and enjoy its rustic look and feel without sacrificing longevity!
One of the main differences between natural veneer and engineered veneer is that engineered products generally require less maintenance overall, as they tend to resist damage better than standard varieties do. This is because of the improved durability features used during the design phases. However, limited refinishing options after your veneer sheets are sliced and glued into blocks means that you need to consider this option carefully before fully committing.
WoodenAve: Affordable Variety of Wood Veneers
Both natural and engineered wood veneers offer great benefits, depending on your project needs and budget constraints. While natural veneer provides unmatched authenticity and character taken directly from real trees and turned into wooden furniture, engineered alternatives deliver consistent quality at lower costs, also making them appealing options.
If you’re looking for affordable options without compromising style or performance, get in touch with WoodenAve! We offer a wide variety of species of wood for natural veneer and high-quality wood for engineered veneer, too.
Natural vs. Engineered Wood Veneer FAQs
Is engineered wood natural or synthetic?
Engineered wood is a synthetic product made by layering wood fibers or veneers. Though it uses wood as a base, the layers are bonded with adhesives and improved with technology veneer processes to imitate natural wood.
What are the most realistic veneers?
Natural veneer production offers the most realistic look since it uses real wood layers. However, high-quality engineered veneers closely imitate natural wood with impressive realism.
What are the disadvantages of engineered wood furniture?
Engineered wood furniture may lack the durability of natural, solid wood and can be prone to moisture damage. Also, some veneer options may not reflect the unique defects of the original wood, giving a less authentic appearance compared to different natural wood types.
Back to Top: Natural vs. Engineered Wood Veneer

Leave A Comment